scanpy.pl.paga#
- scanpy.pl.paga(adata, *, threshold=None, color=None, layout=None, layout_kwds=mappingproxy({}), init_pos=None, root=0, labels=None, single_component=False, solid_edges='connectivities', dashed_edges=None, transitions=None, fontsize=None, fontweight='bold', fontoutline=None, text_kwds=mappingproxy({}), node_size_scale=1.0, node_size_power=0.5, edge_width_scale=1.0, min_edge_width=None, max_edge_width=None, arrowsize=30, title=None, left_margin=0.01, random_state=0, pos=None, normalize_to_color=False, cmap=None, cax=None, colorbar=None, cb_kwds=mappingproxy({}), frameon=None, add_pos=True, export_to_gexf=False, use_raw=True, colors=None, groups=None, plot=True, show=None, save=None, ax=None)[source]#
Plot the PAGA graph through thresholding low-connectivity edges.
Compute a coarse-grained layout of the data. Reuse this by passing
init_pos='paga'toumap()ordraw_graph()and obtain embeddings with more meaningful global topology [Wolf et al., 2019].This uses ForceAtlas2 or igraph’s layout algorithms for most layouts [Csárdi and Nepusz, 2006].
- Parameters:
- adata
AnnData Annotated data matrix.
- threshold
float|None(default:None) Do not draw edges for weights below this threshold. Set to 0 if you want all edges. Discarding low-connectivity edges helps in getting a much clearer picture of the graph.
- color
str|Mapping[str|int,Mapping[Any,float]] |None(default:None) Gene name or
obsannotation defining the node colors. Also plots the degree of the abstracted graph when passing {'degree_dashed','degree_solid'}.Can be also used to visualize pie chart at each node in the following form:
{<group name or index>: {<color>: <fraction>, ...}, ...}. If the fractions do not sum to 1, a new category called'rest'colored grey will be created.- labels
str|Sequence[str] |Mapping[str,str] |None(default:None) The node labels. If
None, this defaults to the group labels stored in the categorical for whichpaga()has been computed.- pos
ndarray|Path|str|None(default:None) Two-column array-like storing the x and y coordinates for drawing. Otherwise, path to a
.gdffile that has been exported from Gephi or a similar graph visualization software.- layout
Union[Literal['fr','drl','kk','grid_fr','lgl','rt','rt_circular','fa'],Literal['eq_tree'],None] (default:None) Plotting layout that computes positions.
'fa'stands for “ForceAtlas2”,'fr'stands for “Fruchterman-Reingold”,'rt'stands for “Reingold-Tilford”,'eq_tree'stands for “eqally spaced tree”. All but'fa'and'eq_tree'are igraph layouts. All other igraph layouts are also permitted. See also parameterposanddraw_graph().- layout_kwds
Mapping[str,Any] (default:mappingproxy({})) Keywords for the layout.
- init_pos
ndarray|None(default:None) Two-column array storing the x and y coordinates for initializing the layout.
- random_state
int|None(default:0) For layouts with random initialization like
'fr', change this to use different intial states for the optimization. IfNone, the initial state is not reproducible.- root
int|str|Sequence[int] |None(default:0) If choosing a tree layout, this is the index of the root node or a list of root node indices. If this is a non-empty vector then the supplied node IDs are used as the roots of the trees (or a single tree if the graph is connected). If this is
Noneor an empty list, the root vertices are automatically calculated based on topological sorting.- transitions
str|None(default:None) Key for
.uns['paga']that specifies the matrix that stores the arrows, for instance'transitions_confidence'.- solid_edges
str(default:'connectivities') Key for
.uns['paga']that specifies the matrix that stores the edges to be drawn solid black.- dashed_edges
str|None(default:None) Key for
.uns['paga']that specifies the matrix that stores the edges to be drawn dashed grey. IfNone, no dashed edges are drawn.- single_component
bool(default:False) Restrict to largest connected component.
- fontsize
int|None(default:None) Font size for node labels.
- fontoutline
int|None(default:None) Width of the white outline around fonts.
- text_kwds
Mapping[str,Any] (default:mappingproxy({})) Keywords for
text().- node_size_scale
float(default:1.0) Increase or decrease the size of the nodes.
- node_size_power
float(default:0.5) The power with which groups sizes influence the radius of the nodes.
- edge_width_scale
float(default:1.0) Edge with scale in units of
rcParams['lines.linewidth'].- min_edge_width
float|None(default:None) Min width of solid edges.
- max_edge_width
float|None(default:None) Max width of solid and dashed edges.
- arrowsize
int(default:30) For directed graphs, choose the size of the arrow head head’s length and width. See :py:class:
matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatchfor attributemutation_scalefor more info.- export_to_gexf
bool(default:False) Export to gexf format to be read by graph visualization programs such as Gephi.
- normalize_to_color
bool(default:False) Whether to normalize categorical plots to
coloror the underlying grouping.- cmap
str|Colormap|None(default:None) The color map.
- cax
Axes|None(default:None) A matplotlib axes object for a potential colorbar.
- cb_kwds
Mapping[str,Any] (default:mappingproxy({})) Keyword arguments for
Colorbar, for instance,ticks.- add_pos
bool(default:True) Add the positions to
adata.uns['paga'].- title
str|None(default:None) Provide a title.
- frameon
bool|None(default:None) Draw a frame around the PAGA graph.
- plot
bool(default:True) If
False, do not create the figure, simply compute the layout.- save
bool|str|None(default:None) If
Trueor astr, save the figure. A string is appended to the default filename. Infer the filetype if ending on {'.pdf','.png','.svg'}.- ax
Axes|None(default:None) A matplotlib axes object.
- adata
- Return type:
- Returns:
If
show==False, one or moreAxesobjects. Adds'pos'toadata.uns['paga']ifadd_posisTrue.
Examples
import scanpy as sc adata = sc.datasets.pbmc3k_processed() sc.tl.paga(adata, groups='louvain') sc.pl.paga(adata)
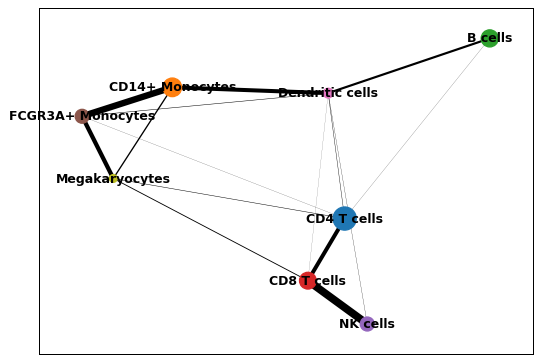
You can increase node and edge sizes by specifying additional arguments.
sc.pl.paga(adata, node_size_scale=10, edge_width_scale=2)
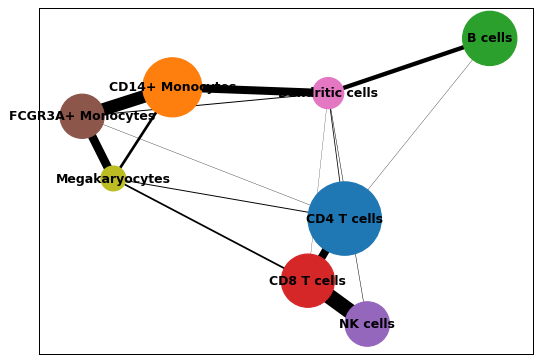
Notes
When initializing the positions, note that – for some reason – igraph mirrors coordinates along the x axis… that is, you should increase the
maxiterparameter by 1 if the layout is flipped.See also